|
Production
planning is
the organization
of production
activities to
meet customer
demands and to
use resources
such as
machinery,
equipment and
workforce in the
production
environment in
line with the
performance
goals of
manufacturers.
Production
planning is a
critical
business process
for
manufacturing
organizations.
Therefore,
manufacturers
need a
production
planning process
that is designed
and successfully
implemented to
meet both their
customers'
expectations and
their own
organizational
goals.
The prepared
production plan
is a future
projection of
output
quantities of
manufacturing
processes in a
timely manner.

What to consider
when preparing a
production plan?
Main concerns to
be considered in
order to prepare
a successful
production plan
are organized in
the table below.
|
Main Concerns |
Related
Factors
(data/knowledge) |
|
Customer
demand |
●
Customer orders,
quantities, due
dates, urgencies
●
Demand forecasts
|
|
Inventory |
●
Safety inventory
levels
●
Raw material,
semi-finished
and finished
good inventory
●
Work-in-process
inventory
|
|
Released
orders |
●
Released
production
orders
●
Released
purchase orders
|
|
Resources |
●
Resource
availability,
capacities,
existing
workloads
●
Resource
eligibilities
●
Availability of
manufacturing
elements (molds,
tools, etc.)
●
Workforce
related
constraints (head
count,
shifts,
overtime, etc.)
●
Manufacturing
lot sizes,
setups,
standard
times
|
|
Transfer
or
Transport |
●
Transfer
capacities and
times
●
Transfer
lot sizes
|
|
Products |
●
Bills of
materials, BOMs
●
Standard unit
times
|
|
Strategies,
tactics |
●
Manufacturing
strategies
(make-to-stock,
make-to-order,
etc.)
●
Planning
tactics
(chasing,
smoothing,
etc.)
●
Key
performance
indicators
(OTIF,
etc.)
and
targets |
|
Supply
chain
operations |
●
Purchasing
priorities,
constraints
and
costs
●
Manufacturing
priorities,
constraints
and
costs
●
Warehousing
priorities,
constraints
and
costs
●
Logistics
priorities,
constraints
and
costs |
More
factors can be added to the above list, for a particular organization.
Increased number of factors
affecting production planning proess makes it a difficult task to be
accomplished in an effective way.
Organizations that have the
capabilities to plan their production better than their competition will
achieve sustainable growth in their market shares, expand product and
customer portfolios and gain cost advantages through reliable duedates
and delivery times they offer to their customers.
Therefore,
an organization's production planning process is a major pillar for its
sustainable profitability.
'Production
planning forms a
balance between
demands and
resources,
through
decisions
focused on
competition and
profitability.'

What decisions
are made in
production
planning?
Üretim ortamının
işleyişi ile ilgili hem
uzun, hem de kısa vadede
pek çok karar üretim
planlamanın kapsamında
düşünülebilir. Aşağıdaki
tabloda üretim planlama
kapsamında
değerlendirilebilecek
veya üretim planlama ile
doğrudan ilişkili bazı
karar örnekleri ve
süreçleri
sınıflandırılmıştır.
Many decisions regarding
the operation of the
production environment,
both in short, medium
and long terms, can be
considered within the
scope of production
planning.
The below table, we
provide a classification
of exemplary processes
and decisions that are
within the context of
(or closely related to)
production planning
|
Long
Term
'Strategic'
Decisions: |
|
Strategic
Business and
Investment
Planning
● Changes
in installed
manufacturing
capacity
● New
facility
construction,
acquisition of
an existing
facility
● New
machinery and
equipment
investments,
etc.
|
|
Medium
Term
'Tactical'
Decisions:
|
|
Sales and
Operations
Planning
(S&OP/IBP),
Budgeting
● Determination
of critical
(bottleneck)
capacity
requirements
●
Procurement of
materials with
long lead times
●
Inventory
and/oor backlog
projections
●
Supply chain
collaborations
(CPFR)
●
Creating
alternative
supply
scenarios, etc.
Article:
'What is Sales
and Operations
Planning
(S&OP/IBP)?'
|
|
Short
Term
'Operational'
Decisions: |
|
Production
Planning
● Production
planning (MPS),
capacity control
(RCCP),
determine due
dates,
●
Speeding up
urgent works,
delaying
non-urgent ones
Article:
'What is
Production
Planning?'
Order
Management,
●
Determine
available-to-promise
(ATP), etc.
●
Determine
capable-to-promise
(CTP), etc.
Material
Planning,
● Determine raw
material and
semi-finished
good
requirements
(MRP)
Upcoming
Article: 'What
is Materials
Planning?'
Detailed
Capacity
Planning,
● Determine
supplier and
production
facilities
capacity
requirements
(CRP)
● Resource/line
balancing,
bottleneck
detection and
management
(TOC), etc.
|
|
Very
Short Term,
'Now' Decisions: |
|
Detailed
Scheduling,
● Scheduling
(determining the
start and end
times of
production
processes)
●
Setup decisions
●
Selecting routes
and resources
from
alternatives
●
Determination of
transfer lot
sizes
●
Updating
schedules
(rescheduling),
etc.
Upcoming
Article:
'What is
Detailed
Scheduling?'
|
|
Abbreviations:
S&OP: Sales
and Operations Planning
IBP:
Integrated Business
Planning
CPFR:
Collaborative Planning,
Forecasting and
Replenishment
MPS: Master
Production Scheduling
RCCP: Rough-Cut
Capacity Planning
ATP:
Available-To-Promise
CTP:
Capable-To-Promise
MRP: Material
Requirements Planning
CRP: Capacity
Requirements Planning
TOC: Theory of
Constraints
|
|
|
|
What are the objectives in
production planning?
The keys to customer satisfaction and
meeting service levels are
not missing duedates in
make-to-order (MTO), and not stocking-out in make-to-stock (MTS).
On the other hand, the costs
of primary supply chain operations such as purchasing, manufacturing,
warehousing and logistics should be all be minimized. Therefore,
production planning decisions should be taken in a way that minimizes
all such costs while meeting the required service levels.
Organizations can and should reduce
purchasing,
manufacturing and inventory costs
via production
planning...
Company X considers this and that, why not we do the same...
Is production planning the same in every organization?
There are basic practices and factors that are described as 'must's in production planning.
However, in every
organizations there are differentiating issues such as manufacturing
strategies, products and their characteristics, physical structure of
the manufacturing environment,
materials,
procurement alternatives,
supply chain relations,
patterns and
trends of customer demand. All these issues and more
affects organization's
competitiveness and therefore should be considered from that
organization's perspective in its production planning process.
The basic approach in
designing organization-based production planning process relies on
organizing planning activities in different planning horizons such as
long, medium and short term, at corresponding levels of item details
such as product groups, products, semi-products or operations,
determining objectives, constraints and priorities, and making
assumptions, when necessary.
For all these reasons,
production planning processes should be designed as tailor- or
custom-made for organizations.
Üretim planlama, kurumsal kaynak planlamanın neresindedir?
Enterprise
resource
planning (ERP)
can be defined
as the
management of
main business
processes in an
integrated and
coordinated
manner within an
organization.
Main business
processes, in
this respect,
can be listed as
sales,
manufacturing,
supply chain,
purchasing,
finance, HR,
etc.
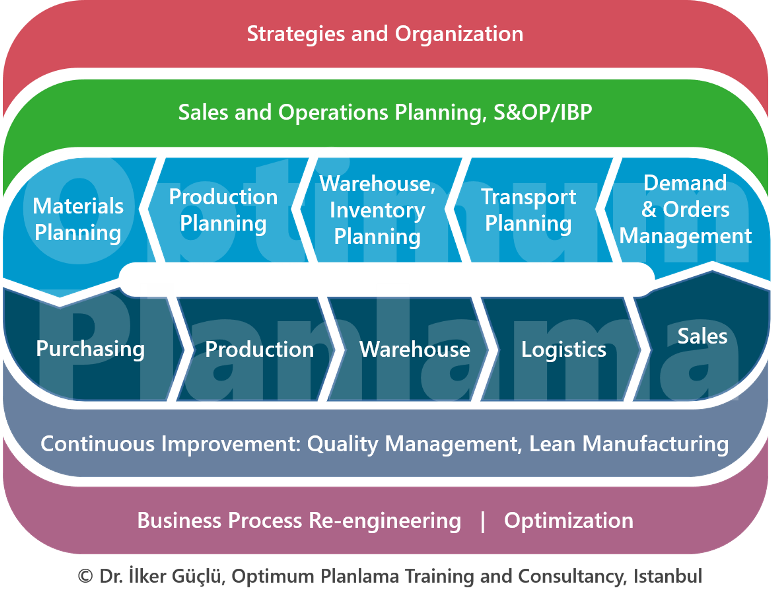
Production
planning holds a
critical
position within
the scope of
supply chain
management. On
the other hand,
production
planning is
directly related
to functions
such as sales,
production,
warehouse,
logistics,
purchasing and
finance.
Organizations striving for
excellence in
their supply
chains, and
therefore in
production
planning,
need certain
functional
planning
processes in
place. These
processes are
outlined below.
For more
knowledge on
these functions,
Upcoming Article:
'What is Supply
Chain
Management?'
|
Is
production
planning
affected
by other
planning
activities?
The
factors
listed
at the
beginning
of the
article,
it is
not
enough
to
consider
only the
manufacturing
environment
when
planning
production.
Customer
orders,
market
dynamics,
purchasing,
warehousing
and
inventory,
distribution
and
logistics
related
many
factors
must
also be
taken
into
account.
The
inability
to
coordinate
the
production
planning
process
with
sales,
production,
purchasing,
warehouse,
logistics,
etc.
affects
delivery
performance
and
profitability
due to
deficiencies
in
meeting
customer
demands
and
resource
utilizations.
Therefore,
production
planning
should
not be
considered
independently
of other
processes,
and the
relations
in
between
should
be
clearly
established
within
the
organization.
Relations
with
Order
Management,
Sales
and
Demand
Planning:
High
deviations
in
demand
forecasts,
frequent
changes
in
orders,
order
cancellations,
urgent
orders,
very
urgent
orders,
very
very
urgent
orders
(!)
adversely
affect
the
overall
purchasing,
production,
storage
and
logistics
processes
of the
institution.
Effective
coordination
of
demand
planning
and
production
planning
is
necessary
for
customer
satisfaction
and the
utilization
of
resources
and
materials
in
correct
work
orders.
For more
information
on
Demand
Planning
and
Sales
Forecasting,
Article:
'What is
Demand
Planning?'
Relations
with
Purchasing
and
Inventory:
It is
not
possible
to
consider
manufacturing
independent
from
inventory.
The raw
materials
and
components
to be
used in
manufacturing
must be
supplied
in a way
that
does not
disrupt
the
production
plans.
In order
to avoid
fluctuations
in
demand
and
supply
in
make-to-stock
environments,
end
product
inventory
should
also be
effectively
planned.
For more
information
on this
topic,
Upcoming
Article:
'What is
Inventory
Optimization?'
Relations
with
Warehousing
and
Logistics:
Critical
issues
in
warehouses
are
storage,
order
preparation
and
loading-unloading
capacities
of
manufacturing
outputs,
as well
as
related
costs.
Logistics
planning
processes, where
material
transfers to
desired
locations in
distribution
channels are
organized, focus
on determining
transportation
schedules, modes
of
transportation
and routing of
manufacturing
outputs.
Therefore,
warehousing and
logistics
constraints and
priorities can
and should
affect an
organization's
production
plans.
For more
detailed
information on
these topics,
Upcoming
Article: 'What
is Inventory
Planning?'
Upcoming
Article: 'What
is Logistics
Planning?'
What are
the
innovative
optimization
approaches
in
production
planning?
Thanks to the
advances in
information
technologies,
the
implementation
of innovative
techniques in
production
planning is
gaining
popularity over
time.
These innovative
approaches use
various
optimization
techniques
developed within
the scope of
Operations
Research.
Thanks to these
techniques,
planning
decisions can be
made that ensure
customer
satisfaction,
increase the
utilization of
resources, and
minimize costs,
all at the same
time.
For more
information on
optimization,
Upcoming
Article: 'What
is
optimization?'
In processes
such as
production
planning, where
a large number
of concerns and
factors are in
place, manual
efforts that use
trial and error
usually requires
a lot of effort
and a lot of
time.
On the other
hand, innovative
techniques
applied in
preparing
production plans
offer better (or
the best)
solutions to
these complex
problems, in
relatively much
shorter times.
Organizations
need to identify
the deficiencies
and requirements
of their current
production
planning
processes, and
then improve or
re-engineer
them.
Optimum
Planlama
offers
professional
training and
consultancy
services for
organizations to
excel their
supply chain
performance.
Dr. İlker Güçlü
|
Founder,
Optimum Planlama
|
Click
for resume
This
article
is to
provide
a
general
information.
The
aforementioned
may not
apply to
all
organizations.
Optimum Planlama training programs focused on
'Production Planning' business processes are,
|
Production Planning and
Detailed Scheduling
training
program
(V4.0EN)
|
|
 |
|
Training
Goals
On-time deliveries and
service levels,
stock-out or shortage
prevention, optimizing inventory levels,
capacity considerations,
profitability, efficiency,
etc... these are all
critical and
'conflicting' aspects in supply and
manufacturing operations.
The program presents
basic knowledge and
skills for the
generation of production
and material planning,
as well as detailed
scheduling processes
that can effectively
form a balance between
these critical aspects
of these environments.
Processes, signals and
information flows,
planning and
optimization techniques
will be discussed with
in-class exercises.
This training program
has been presented 100+
times to 1000+ employees
from 300+
organizations.
Verbal presentation, all
visuals and printed
material are in English.
Click for
details. |
Target Audience
Supply
Chain
Management
Manufacturing
Planning and
Control
Operations
Management
Order Management
Operations,
Factory
Management
Purchasing and
Replenishment
Materials,
Capacity
Management
Information
Technologies
Subcontractor
Management
Career
seekers in
Planning
|
Training
Modules
|
Day
1:
Master Scheduling
and Order Management |
Day 2:
Materials and Capacity
Planning
|
|
Competition and Profit
Focus in Planning
Long and Medium Term
Production Planning
Demand Planning and Order
Management
Master Production
Scheduling, MPS
Backlog and Overloaded
Plans
When to Update & NOT to update the
Master Schedule?
In-Class Exercises
Available/Capable to
Promise, ATP/CTP
Flowshop / Jobshop,
Make-to-Stock /
Make-to-Order
Capacity and Bottlenecks
Management, RCCP
Material Planning: MRP
or Kanban?
Performance Indicators
in Production Planning
How to Optimize
Production Planning
Decisions?
In-Class Exercises
|
Material Requirements
Planning, MRP
Bill of Materials, MRP
Explosion, Time
Offsetting
Material Planning in
Make-to-Order
Co-Products,
By-Products, Recovered
Materials
Order Quantities in
Purchasing/Production
Capacity Requirements
Planning, CRP
In-Class Exercises
Capacity Planning by
Production Environment
Theory of Constraints,
TOC, Bottleneck Planning
Lean Manufacturing,
Wastes, Line Balancing
Technologies Selection:
ERP, APS
Performance Indicators
in Material Planning
How to Optimize Material
Planning Decisions?
In-Class Exercises
|
|
Day
3:
Detailed Scheduling
of Work Flows |
Day 4:
Detailed Scheduling
with Advanced Algorithms
|
|
Production Activities
Control, PAC
Cycle Times, Queues,
Setups
Finite-Infinite,
Forward-Backward
Scheduling
Basic Concepts of Detail
Scheduling
Resources, Operational
Constraints, Objectives
Detail Scheduling with
Gantt Charts
In-Class Exercises with
Gantt Charts
Dispatching
Rules in Operation
Sequencing
Decreasing Queues,
Work-In-Process
Inventory
Scheduling with Material
Supply Restrictions
Preventing or Reducing
Delays
How to Minimize Setup
Losses?
Effects of Process
Quality and Lean
Manufacturing
In-Class Exercises with
Gantt Charts
|
Scheduling in Resources
with Similar
Capabilities
Detailed Scheduling of
Flowshop Production
Production Lot Sizes and
Transfer Lots
Detail Scheduling of
Jobshop Production
Alternative Approaches
and Algorithms
Exceptions and
Optimization
In-Class Exercises with
Gantt Charts
How to Determine
Reliable Duedates?
Project Scheduling in
Production, CPM
Optimization with
Heuristic Algorithms
Optimization with
Mathematical Modeling
Optimization with Mixed
Methods
Automation in Detailed
Scheduling
In-Class Exercises
|
Excellence
in your supply
chain
performance,

▲
TOP OF PAGE |